Point of this post: why are patenting officers giving provisional patents when the idea has been described in earlier papers (lack of novelty) and is a logical consequence of earlier work?
Why HRP2 for detection?
Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) HRP epitopes recognised by MAbs
abundance of HRP2 motifs
HRP3
Other useful characteristics of RDT MAbs (malaria)
Conformational epitope vs linear epitope
HRP2 missing!
HRP2 and HRP3 missing in some South American P. falciparum parasites
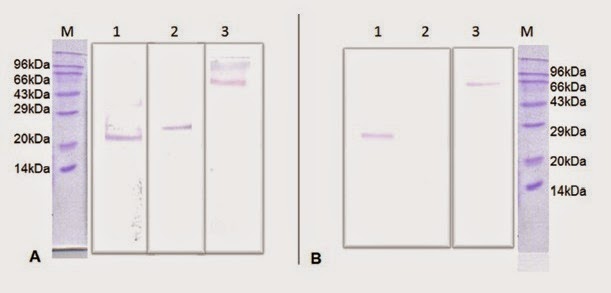
Selection of last 105 amino acids in HRP2 as epitope
band deletions by brightness-contrast adjustments
Why are the lane bands not the same colour as the marker lane?
Too much whitening ....
Lee N., K. T. Andrews, M. L. Gatton, D. Bell, Q. Cheng & J. McCarthy (2006). Effect of Sequence Variation in Plasmodium falciparum Histidine- Rich Protein 2 on Binding of Specific Monoclonal Antibodies: Implications for Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Malaria, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 44 (8) 2773-2778. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02557-05
Cheng Q., John Barnwell, Peter Chiodini, James McCarthy, David Bell & Jane Cunningham (2014). Plasmodium falciparum parasites lacking histidine-rich protein 2 and 3: a review and recommendations for accurate reporting, Malaria Journal, 13 (1) 283. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-13-283
Verma R., M.A. Vijayalakshmi & Krishnan Venkataraman (2015). Novel monoclonal antibody against truncated C terminal region of Histidine Rich Protein2 (PfHRP2) and its utility for the specific diagnosis of malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, Experimental Parasitology, 150 56-66. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2015.01.001